History: Seven Wonders of the World
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon
The Temple of Artemis at Ephesus
The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus
Stonehenge and the Rings of Rock
==============================
Introduction
Although most people know that a list exists of the Seven World Wonders, only few can name them. The list of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World was originally compiled around the second century BC. The first reference to the idea is found in History of Herodotus as long ago as the 5th century BC. Decades later, Greek historians wrote about the greatest monuments at the time. Callimachus of Cyrene (305BC-240BC), Chief Librarian of the Alexandria Mouseion, wrote “A Collection of Wonders around the World”. All we know about the collection is its title, for it was destroyed with the Alexandria Library.
The final list of the Seven Wonders was compiled during the Middle Ages. The list comprised the seven most impressive monuments of the Ancient World, some of which barely survived to the Middle Ages. Others did not even co-exist. Among the oldest references to the canonical list are the engravings by the Dutch artist Maerten van Heemskerck (1498-1574), and Johann Fischer von Erlach’s History of Architecture.
Today, archaeological evidence reveals some of the mysteries that surrounded the history of the Wonders for centuries. For their builders, the Seven Wonders were a celebration of religion, mythology, art, power, and science. For us, they reflect the ability of humans to change the surrounding landscape by building massive yet beautiful structures, one of which stood the test of time to this very day.
==============================
The Great Pyramid of Giza

A gigantic stone structure near the ancient city of Memphis, serving as a tomb for the Egyptian Pharaoh Khufu
Man fears Time, yet Time fears the Pyramids
--Arab proverb
It is the one and only Wonder which does not require a description by early historians and poets. It is the one and only Wonder that does not need speculations concerning its appearance, size, and shape. It is the oldest, yet it is the only surviving of the Seven Ancient Wonders. It is the Great Pyramid of Giza.
Location
At the city of Giza, a necropolis of ancient Memphis, and today part of Greater Cairo, Egypt.
History
Contrary to the common belief, only the Great Pyramid of Khufu (Cheops), not all three Great Pyramids, is on top of the list of Wonders. The monument was built by the Egyptian pharaoh Khufu of the Fourth Dynasty around the year 2560 BC to serve as a tomb when he dies. The tradition of pyramid building started in Ancient Egypt as a sophistication of the idea of a mastaba or “platform” covering the royal tomb. Later, several stacked mastabas were used. Early pyramids, such as the Step Pyramid of King Zoser (Djoser) at Saqqara by the famous Egyptian architect, Imhotep, illustrate this connection.
The great pyramid is believed to have been built over a 20 year period. The site was first prepared, and blocks of stone were transported and placed. An outer casing (which disappeared over the years) was then used to smooth the surface. Although it is not known how the blocks were put in place, several theories have been proposed. One theory involves the construction of a straight or spiral ramp that was raised as the construction proceeded. This ramp, coated with mud and water, eased the displacement of the blocks which were pushed (or pulled) into place. A second theory suggests that the blocks were placed using long levers with a short angled foot.
Throughout their history, the pyramids of Giza have stimulated human imagination. They were referred to as “The Granaries of Joseph” and “The Mountains of Pharaoh”. When Napoleon invaded Egypt in 1798, his pride was expressed through his famous quote: “Soldats! Du haut de ces Pyramides, 40 siècles nous contemplent”. (Soldiers! From the top of these Pyramids, 40 centuries are looking at us)
Today, the Great Pyramid is enclosed, together with the other pyramids and the Sphinx, in the touristic region of the Giza Plateau. Also in the area is the museum housing the mysterious Sun Boat, only discovered in 1954 near the south side of the pyramid. The boat is believed to have been used to carry the body of Khufu in his last journey on earth before being buried inside the pyramid. It may also serve him as a means of transportation in his afterlife journey according to Ancient Egyptian beliefs.
Description
When it was built, the Great pyramid was 145.75 m (481 ft) high. Over the years, it lost 10 m (30 ft) off its top. It ranked as the tallest structure on Earth for more than 43 centuries, only to be surpassed in height in the nineteenth century AD. It was covered with a casing of stones to smooth its surface (some of the casing can still be seen near the top of Khefre’s pyramid). The sloping angle of its sides is 51 degrees and 51 minutes. Each side is carefully oriented with one of the cardinal points of the compass, that is, north, south, east, and west. The horizontal cross section of the pyramid is square at any level, with each side measuring 229 m (751 ft) in length. The maximum error between side lengths is astonishingly less than 0.1%.
The structure consists of approximately 2 million blocks of stone, each weighing more than two tons. It has been suggested that there are enough blocks in the three pyramids to build a 3 m (10 ft) high, 0.3 m (1 ft) thick wall around France. The area covered by the Great pyramid can accommodate St Peter’s in Rome, the cathedrals of Florence and Milan, and Westminster and St Paul’s in London combined.
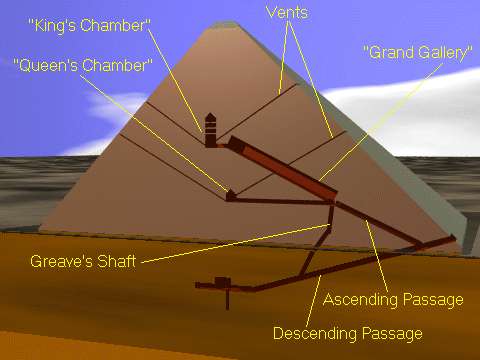
On the north face, is the pyramid’s entrance. A number of corridors, galleries, and escape shafts either lead to the King’s burial chamber, or were intended to serve other functions. The King’s chamber is located at the heart of the pyramid, only accessible through the Great Gallery and an ascending corridor. The King’s sarcophagus is made of red granite, as are the interior walls of the King’s Chamber. Most impressive is the sharp-edged stone over the doorway which is over 3 m (10 ft) long, 2.4 m (8 feet) high and 1.3 m (4 ft) thick. All of the interior stones fit so well, a card won’t fit between them. The sarcophagus is oriented in accordance with the compass directions, and is only about 1 cm smaller in dimensions than the chamber entrance. It might have been introduced as the structure was progressing.
New theories concerning the origin and purpose of the Pyramids of Giza have been proposed... Astronomic observatories... Places of cult worship... Geometric structures constructed by a long-gone civilization... Even extraterrestrial-related theories have been proposed with little evidence in support... The overwhelming scientific and historic evidence still supports the conclusion that, like many smaller pyramids in the region, the Great Pyramids were built by the great Ancient Egyptian civilization off the West bank of the Nile as tombs for their magnificent Kings... Tombs where Khufu, Khefre, and Menkaure could start their mystic journey to the afterlife.
----------------
It’s 756 feet long on each side, 450 high and is composed of 2,300,000 blocks of stone, each averaging 2 1/2 tons in weight. Despite the makers’ limited surveying tools no side is more than 8 inches different in length than another, and the whole structure is perfectly oriented to the points of the compass. Until the 19th century it was the tallest building in the world and, at the age of 4,500 years, it is the only one of the famous “Seven Wonders of the Ancient World” that still stands. It is the Great Pyramid of Khufu, at Giza, Egypt.
Some of the earliest history of the Pyramid comes from a Greek traveler named Herodotus of Halicanassus. He visited Egypt around 450 BC and included a description of the Great Pyramid in a history book he wrote. Herodotus was told by his Egyptian guides that it took twenty-years for a force of 100,000 oppressed slaves to build the pyramid. Stones were lifted into position by the use of immense machines. The purpose of the structure, according to Herodotus’s sources, was as a tomb for the Pharaoh Khufu (whom the Greeks referred to as Cheops).
Most of what Herodotus tells us is probably false. Scientists calculate that fewer men and less years were needed than Herodotus suggests. It also seems unlikely that slaves or complicated machines were needed for the pyramid construction. It isn’t surprising that the Greek historian got it wrong. By the time he visited the site the great pyramid was already 20 centuries old, and much of the truth about it was shrouded in the mists of history.
Certainly the idea that it was a tomb for a Pharaoh, though, seems in line with Egyptian practices. For many centuries before and after the construction of the Great Pyramid the Egyptians had interned their dead Pharaoh-Kings, whom they believed to be living Gods, in intricate tombs. Some were above ground structures, like the pyramid, others were cut in the rock below mountains. All the dead leaders, though, were outfitted with the many things it was believed they would need in the after-life to come. Many were buried with untold treasures.
Even in ancient times thieves, breaking into the sacred burial places, were a major problem and Egyptian architects became adept at designing passageways that could be plugged with impassable granite blocks, creating secret, hidden rooms and making decoy chambers. No matter how clever the designers became, though, robbers seemed to be smarter and with almost no exceptions each of the great tombs of the Egyptian Kings were plundered.
In 820 A.D. the Arab Caliph Abdullah Al Manum decided to search for the treasure of Khufu. He gathered a gang of workmen and, unable to find the location of a reputed secret door, started burrowing into the side of the monument. After a hundred feet of hard going they were about to give up when they heard a heavy thud echo through the interior of the pyramid. Digging in the direction of the sound they soon came upon a passageway that descended into the heart of the structure. On the floor lay a large block that had fallen from the ceiling, apparently causing the noise they had heard. Back at the beginning of the corridor they found the secret hinged door to the outside they had missed.
Working their way down the passage they soon found themselves deep in the natural stone below the pyramid. The corridor stopped descending and went horizontal for about 50 feet, then ended in a blank wall. A pit extended downward from there for about 30 feet, but it was empty.
When the workmen examined the fallen block they noticed a large granite plug above it. Cutting through the softer stone around it they found another passageway that extended up into the heart of the pyramid. As they followed this corridor upward they found several more granite blocks closing off the tunnel. In each case they cut around them by burrowing through the softer limestone of the walls. Finally they found themselves in a low, horizontal passage that lead to a small, square, empty room. This became known as the “Queen’s Chamber,” though it seems unlikely that it ever served that function.
Back at the junction of the ascending and descending passageways, the workers noticed an open space in the ceiling. Climbing up they found themselves in a high-roofed, ascending passageway. This became known as the “Grand Gallery.” At the top of the gallery was a low horizontal passage that led to a large room, some 34 feet long, 17 feet wide, and 19 feet high, the “King’s Chamber.” In the center was a huge granite sarcophagus without a lid. Otherwise the room was completely empty.
The Arabs, as if in revenge for the missing treasure, stripped the pyramid of it’s fine white limestone casing and used it for building in Cairo. They even attempted to disassemble the great pyramid itself, but after removing the top 30 feet of stone, they gave up on this impossible task.
So what happened to the treasure of King Khufu? Conventional wisdom says that, like so many other royal tombs, the pyramid was the victim of robbers in ancient times. If we believe the accounts of Manum’s men, though, the granite plugs that blocked the passageways were still in place when they entered the tomb. How did the thieves get in and out?
In 1638 a English mathematician, John Greaves, visited the pyramid. He discovered a narrow shaft, hidden in the wall, that connected the Grand Gallery with the descending passage. Both ends were tightly sealed and the bottom was blocked with debris. Some archaeologists suggested this route was used by the last of the Pharaoh’s men to exit the tomb, after the granite plugs had been put in place, and by the thieves to get inside. Given the small size of the passageway and the amount of debris it seems unlikely that the massive amount of treasure, including the huge missing sarcophagus lid, could have been removed this way.
Some have suggested that the pyramid was never meant as a tomb, but as an astronomical observatory. The Roman author Proclus, in fact, states that before the pyramid was completed it did serve in this function. We can’t put two much weight on Proclus words, though, remembering that when he advanced his theory the pyramid was already over 2000 years old.
Richard Proctor, an astronomer, did observe that the descending passage could have been used to observe the transits of certain stars. He also suggested that the grand gallery, when open at the top, during construction, could have been used for mapping the sky.
Many strange, and some silly, theories have arisen over the years to explain the pyramid and it’s passageways. Most archaeologists, though, accept the theory that the great pyramid was just the largest of a tradition of tombs used for the Pharaohs of Egypt.
So what happened to Khufu’s mummy and treasure? Nobody knows. Extensive explorations have found no other chambers or passageways. Still one must wonder if, perhaps in this one case, the King and his architects out smarted both the ancient thieves and modern archaeologists and that somewhere in, or below, the last wonder of the ancient world, rests Khufu and his sacred gold.


The pyramids at Giza. The far pyramid is the “Great Pyramid.” The middle one looks larger, but only because it is built on higher ground.
==============================
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon
A palace with legendary gardens built on the banks of the Euphrates river by King Nebuchadnezzar II
The approach to the Garden sloped like a hillside and the several parts of the structure rose from one another tier on tier... On all this, the earth had been piled... and was thickly planted with trees of every kind that, by their great size and other charm, gave pleasure to the beholder... The water machines [raised] the water in great abundance from the river, although no one outside could see it.
-- Diodorus Siculus
Fruits and flowers... Waterfalls... Gardens hanging from the palace terraces... Exotic animals... This is the picture of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon in most people’s minds. It may be surprising to know that they might have never existed except in the minds of Greek poets and historians!
Location
On the east bank of the River Euphrates, about 50 km south of Baghdad, Iraq.
History
The Babylonian kingdom flourished under the rule of the famous King, Hammurabi (1792-1750 BC). It was not until the reign of Naboplashar (625-605 BC) of the Neo-Babylonian dynasty that the Mesopotamian civilization reached its ultimate glory. His son, Nebuchadnezzar II (604-562 BC) is credited for building the legendary Hanging Gardens. It is said that the Gardens were built by Nebuchadnezzar to please his wife or concubine who had been “brought up in Media and had a passion for mountain surroundings”.
While the most descriptive accounts of the Gardens come from Greek historians such as Berossus and Diodorus Siculus, Babylonian records stay silent on the matter. Tablets from the time of Nebuchadnezzar do not have a single reference to the Hanging Gardens, although descriptions of his palace, the city of Babylon, and the walls are found. Even the historians who give detailed descriptions of the Hanging Gardens never saw them. Modern historians argue that when Alexander’s soldiers reached the fertile land of Mesopotamia and saw Babylon, they were impressed. When they later returned to their rugged homeland, they had stories to tell about the amazing gardens and palm trees at Mesopotamia.. About the palace of Nebuchadnezzar.. About the Tower of Babel and the ziggurats. And it was the imagination of poets and ancient historians that blended all these elements together to produce one of the World Wonders.
It wasn’t until the twentieth century that some of the mysteries surrounding the Hanging Gardens were revealed. Archaeologists are still struggling to gather enough evidence before reaching the final conclusions about the location of the Gardens, their irrigation system, and their true appearance. Some recent researchers even suggest that the Hanging Gardens were built by Senaherib, not by Nebuchadnezzar II (ca. 100 years earlier).
Description
Detailed descriptions of the Gardens come from ancient Greek sources, including the writings of Strabo and Philo of Byzantium. Here are some excerpts from their accounts:
“The Garden is quadrangular, and each side is four plethra long. It consists of arched vaults which are located on checkered cube-like foundations.. The ascent of the uppermost terrace-roofs is made by a stairway...”
“The Hanging Garden has plants cultivated above ground level, and the roots of the trees are embedded in an upper terrace rather than in the earth. The whole mass is supported on stone columns... Streams of water emerging from elevated sources flow down sloping channels... These waters irrigate the whole garden saturating the roots of plants and keeping the whole area moist. Hence the grass is permanently green and the leaves of trees grow firmly attached to supple branches... This is a work of art of royal luxury and its most striking feature is that the labor of cultivation is suspended above the heads of the spectators”.
More recent archaeological excavations at the ancient city of Babylon in Iraq uncovered the foundation of the palace. Other findings include the Vaulted Building with thick walls and an irrigation well near the southern palace. A group of archaeologists surveyed the area of the southern palace and reconstructed the Vaulted Building as the Hanging Gardens. However, the Greek historian Strabo had stated that the gardens were situated by the River Euphrates. So others argue that the site is too far from the Euphrates to support the theory since the Vaulted Building is several hundreds of meters away. They reconstructed the site of the palace and located the Gardens in the area stretching from the River to the Palace. On the river banks, recently discovered massive walls 25 m thick may have been stepped to form terraces... the ones described in Greek references.
----------------
The ancient city of Babylon, under King Nebuchadnezzar II, must have been a wonder to the traveler’s eyes. “In addition to its size,” wrote Herodotus, a historian in 450 BC, “Babylon surpasses in splendor any city in the known world.”
Herodotus claimed the outer walls were 56 miles in length, 80 feet thick and 320 feet high. Wide enough, he said, to allow a four-horse chariot to turn. The inner walls were “not so thick as the first, but hardly less strong.” Inside the walls were fortresses and temples containing immense statues of solid gold. Rising above the city was the famous Tower of Babel, a temple to the god Marduk, that seemed to reach to the heavens.
While archaeological examination has disputed some of Herodotus’s claims (the outer walls seem to be only 10 miles long and not nearly as high) his narrative does give us a sense of how awesome the features of the city appeared to those that visited it. Interestingly enough, though, one of the city’s most spectacular sites is not even mentioned by Herodotus: The Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
Accounts indicate that the garden was built by King Nebuchadnezzar, who ruled the city for 43 years starting in 605 BC (There is a less-reliable, alternative story that the gardens were built by the Assyrian Queen Semiramis during her five year reign starting in 810 BC). This was the height of the city’s power and influence and King Nebuchadnezzar constructed an astonishing array of temples, streets, palaces and walls.
According to accounts, the gardens were built to cheer up Nebuchadnezzar’s homesick wife, Amyitis. Amyitis, daughter of the king of the Medes, was married to Nebuchadnezzar to create an alliance between the nations. The land she came from, though, was green, rugged and mountainous, and she found the flat, sun-baked terrain of Mesopotamia depressing. The king decided to recreate her homeland by building an artificial mountain with rooftop gardens.
The Hanging Gardens probably did not really “hang” in the sense of being suspended from cables or ropes. The name comes from an inexact translation of the Greek word kremastos or the Latin word pensilis, which mean not just “hanging”, but “overhanging” as in the case of a terrace or balcony.
The Greek geographer Strabo, who described the gardens in first century BC, wrote, “It consists of vaulted terraces raised one above another, and resting upon cube-shaped pillars. These are hollow and filled with earth to allow trees of the largest size to be planted. The pillars, the vaults, and terraces are constructed of baked brick and asphalt.”
“The ascent to the highest story is by stairs, and at their side are water engines, by means of which persons, appointed expressly for the purpose, are continually employed in raising water from the Euphrates into the garden.”
Strabo touchs on what, to the ancients, was probably the most amazing part of the garden. Babylon rarely received rain and for the garden to survive it would have had to been irrigated by using water from the nearby Euphrates River. That meant lifting the water far into the air so it could flow down through the terraces, watering the plants at each level. This was probably done by means of a “chain pump.”
A chain pump is two large wheels, one above the other, connected by a chain. On the chain arehung buckets. Below the bottom wheel is a pool with the water source. As the wheel is turned, the buckets dip into the pool and pick up water. The chain then lifts them to the upper wheel, where the buckets are tipped and dumped into an upper pool. The chain then carries the empty ones back down to be refilled.
The pool at the top of the gardens could then be released by gates into channels which acted as artificial streams to water the gardens. The pump wheel below was attached to a shaft and a handle. By turning the handle slaves provided the power to run the contraption.
Construction of the garden wasn’t only complicated by getting the water up to the top, but also by having to avoid having the liquid ruin the foundation once it was released. Since stone was difficult to get on the Mesopotamian plain, most of the architecture in Babel utilized brick. The bricks were composed of clay mixed with chopped straw and baked in the sun. The bricks were then joined with bitumen, a slimy substance, which acted as a mortar. These bricks quickly dissolved when soaked with water. For most buildings in Babel this wasn’t a problem because rain was so rare. However, the gardens were continually exposed to irrigation and the foundation had to be protected.
Diodorus Siculus, a Greek historian, stated that the platforms on which the garden stood consisted of huge slabs of stone (otherwise unheard of in Babel), covered with layers of reed, asphalt and tiles. Over this was put “a covering with sheets of lead, that the wet which drenched through the earth might not rot the foundation. Upon all these was laid earth of a convenient depth, sufficient for the growth of the greatest trees. When the soil was laid even and smooth, it was planted with all sorts of trees, which both for greatness and beauty might delight the spectators.”
How big were the gardens? Diodorus tells us it was about 400 feet wide by 400 feet long and more than 80 feet high. Other accounts indicate the height was equal to the outer city walls. Walls that Herodotus said were 320 feet high.
In any case the gardens were an amazing sight: A green, leafy, artificial mountain rising off the plain. But did it actually exist? After all, Herodotus never mentions it.
This was one of the questions that occurred to German archaeologist Robert Koldewey in 1899. For centuries before that the ancient city of Babel was nothing but a mound of muddy debris. Though unlike many ancient locations, the city’s position was well-known, nothing visible remained of its architecture. Koldewey dug on the Babel site for some fourteen years and unearthed many of its features including the outer walls, inner walls, foundation of the Tower of Babel, Nebuchadnezzar’s palaces and the wide processional roadway which passed through the heart of the city.
While excavating the Southern Citadel, Koldewey discovered a basement with fourteen large rooms with stone arch ceilings. Ancient records indicated that only two locations in the city had made use of stone, the north wall of the Northern Citadel, and the Hanging Gardens. The north wall of the Northern Citadel had already been found and had, indeed, contained stone. This made it seem likely that Koldewey had found the cellar of the gardens.
He continued exploring the area and discovered many of the features reported by Diodorus. Finally a room was unearthed with three large, strange holes in the floor. Koldewey concluded this had been the location of the chain pumps that raised the water to the garden’s roof.
The foundations that Koldewey discovered measured some 100 by 150 feet. Smaller than the measurements described by ancient historians, but still impressive.
While Koldewey was convinced he’d found the gardens, some modern archaeologists call his discovery into question arguing that this location is too far from the river to have be irrigated with the amount of water that would have been required. Also tablets recently found at the site suggest that the location was used for administrative and/or storage purposes, not as a pleasure garden.
Wherever the location of the gardens were, we can only wonder if Queen Amyitis was happy with her fantastic present, or if she continued to pine for the green mountains of her homeland.

==============================
The Statue of Zeus at Olympia

An enormous statue of the Greek father of gods, carved by the great sculptor Pheidias
In his right hand a figure of Victory made from ivory and gold. In his left hand, his scepter inlaid with all metals, and an eagle perched on the sceptre. The sandals of the god are made of gold, as is his robe.
-- Pausanias the Greek (2nd century AD)
This is the statue of the god in whose honor the Ancient Olympic games were held. It was located on the land that gave its very name to the Olympics. At the time of the games, wars stopped, and athletes came from Asia Minor, Syria, Egypt, and Sicily to celebrate the Olympics and to worship their king of gods: Zeus.
Location
At the ancient town of Olympia, on the west coast of modern Greece, about 150 km west of Athens.
History
The ancient Greek calendar starts in 776 BC, for the Olympic games are believed to have started that year. The magnificent temple of Zeus was designed by the architect Libon and was built around 450 BC. Under the growing power of ancient Greece, the simple Doric-style temple seemed too mundane, and modifications were needed. The solution: A majestic statue. The Athenian sculptor Pheidias was assigned for the “sacred” task, reminiscent of Michelangelo’s paintings at the Sistine Chapel.
For the years that followed, the temple attracted visitors and worshippers from all over the world. In the second century BC repairs were skillfully made to the aging statue. In the first century AD, the Roman emperor Caligula attempted to transport the statue to Rome. However, his attempt failed when the scaffolding built by Caligula’s workmen collapsed. After the Olympic games were banned in AD 391 by the emperor Theodosius I as Pagan practices, the temple of Zeus was ordered closed.
Olympia was further struck by earthquakes, landslides and floods, and the temple was damaged by fire in the fifth century AD. Earlier, the statue had been transported by wealthy Greeks to a palace in Constantinople. There, it survived until it was destroyed by a severe fire in AD 462. Today nothing remains at the site of the old temple except rocks and debris, the foundation of the buildings, and fallen columns.
Description
Pheidias began working on the statue around 440 BC. Years earlier, he had developed a technique to build enormous gold and ivory statues. This was done by erecting a wooden frame on which sheets of metal and ivory were placed to provide the outer covering. Pheidias’ workshop in Olympia still exists, and is coincidentally -- or may be not -- identical in size and orientation to the temple of Zeus. There, he sculpted and carved the different pieces of the statue before they were assembled in the temple.
When the statue was completed, it barely fitted in the temple. Strabo wrote:
“.. although the temple itself is very large, the sculptor is criticized for not having appreciated the correct proportions. He has shown Zeus seated, but with the head almost touching the ceiling, so that we have the impression that if Zeus moved to stand up he would unroof the temple.”
Strabo was right, except that the sculptor is to be commended, not criticized. It is this size impression that made the statue so wonderful. It is the idea that the king of gods is capable of unroofing the temple if he stood up that fascinated poets and historians alike. The base of the statue was about 6.5 m (20 ft) wide and 1.0 meter (3 ft) high. The height of the statue itself was 13 m (40 ft), equivalent to a modern 4-story building.
The statue was so high that visitors described the throne more than Zeus body and features. The legs of the throne were decorated with sphinxes and winged figures of Victory. Greek gods and mythical figures also adorned the scene: Apollo, Artemis, and Niobe’s children. The Greek Pausanias wrote:
On his head is a sculpted wreath of olive sprays. In his right hand he holds a figure of Victory made from ivory and gold... In his left hand, he holds a sceptre inlaid with every kind of metal, with an eagle perched on the sceptre. His sandals are made of gold, as is his robe. His garments are carved with animals and with lilies. The throne is decorated with gold, precious stones, ebony, and ivory.
The statue was occasionally decorated with gifts from kings and rulers. the most notable of these gifts was a woollen curtain “adorned with Assyrian woven patterns and Pheonician dye” which was dedicated by the Syrian king Antiochus IV.
Copies of the statue were made, including a large prototype at Cyrene (Libya). None of them, however, survived to the present day. Early reconstructions such as the one by von Erlach are now believed to be rather inaccurate. For us, we can only wonder about the true appearance of the statue -- the greatest work in Greek sculpture.
-------------------
In ancient times the Greeks held one of their most important festivals, The Olympic Games, in honor of the King of their gods, Zeus. Like our modern Olympics, athletes traveled from distant lands, including Asia Minor, Syria, Egypt and Sicily, to compete in the games. The Olympics were first started in 776 B.C. and held at a shrine to Zeus located on the western coast of Greece in a region called Peloponnesus. The games, held every four years, helped to unify the Greek city-states. Sacred truce was declared during the games and wars were stopped. Safe passage was given to all traveling to the site, called Olympia, for the season of the games.
The site consisted of a stadium (for the games) and a sacred grove, or Altis, where temples were located. The shrine to Zeus was simple in the early years, but as time went by and the games increased in importance, it became obvious that a new, larger temple, one worthy of the King of the gods, was needed. Between 470 and 460 B.C., construction on a new temple was started. The designer was Libon of Elis and his masterpiece, The Temple of Zeus, was completed in 456 B.C..
This temple followed a design used on many large Grecian temples. It was similar to the Parthenon in Athens and the Temple of Artemis in Ephesus. The temple was built on a raised, rectangular platform. Thirteen large columns supported the roof along the sides and six supported it on each end. A gently-peaked roof topped the building. The triangles, or “pediments,” created by the sloped roof at the ends of the building were filled with sculpture. Under the pediments, just above the columns, was more sculpture depicting the twelve labors of Heracles, six on each end.
Though the temple was considered one of the best examples of the Doric design because of its style and the quality of the workmanship, it was decided the temple alone was too simple to be worthy of the King of the gods. To remedy this, a statue was commissioned for the interior- a magnificent statue of Zeus that would become one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
The sculptor chosen for this great task was a man named Phidias. He had already rendered a forty-foot high statue of the goddess Athena for the Parthenon in Athens and had also done much of the sculpture on the exterior of that temple. After his work in Athens was done, Phidias traveled to Olympia to start on what was considered his best work, the statue of Zeus. On arriving he set up a workshop to the west of the temple.
According to accounts, the statue was located at the western end of the temple. It was 22 feet wide and some 40 feet tall. The figure of Zeus was seated on an elaborate throne. His head nearly grazed the roof. The historian Strabo wrote, “...although the temple itself is very large, the sculptor is criticized for not having appreciated the correct proportions. He has depicted Zeus seated, but with the head almost touching the ceiling, so that we have the impression that if Zeus moved to stand up he would unroof the temple...”
Others who viewed that temple disagreed with Strabo and found the proportions very effective in conveying the god’s size and power. By filling nearly all the available space, the statue was made to seem even larger than it really was.
In its right hand the statue held the figure of Nike (the goddess of victory) and in its left was a scepter “inlaid with every kind of metal...” which was topped with an eagle. Perhaps even more impressive than the statue itself was the throne made out of gold, ebony, ivory and inlaid with precious stones. Carved into the chair were figures of Greek gods and mystical animals, like the sphinx.
The figure’s skin was composed of ivory and the beard, hair and robe of gold. Construction was by the use of gold and ivory plates attached to a wooden frame. Because the weather in Olympia was so damp, the statue required care so that the humidity would not crack the ivory. For this purpose it was constantly treated with oil kept in a special pool in the floor of the temple. It is said that for centuries the decedents of Phidias held the responsibility for this maintenance of the statue.
Besides the statue, there was little inside the temple. The Greeks preferred the interior of their shrines to be simple. The feeling it gave was probably very much like the Lincoln Memorial(Left above and right below) or Jefferson Memorial in Washington, D.C. with their lofty marble columns and single, large statues.
Copies of the statue were made, but none survive, though pictures found on coins give researchers clues about its appearance.
Despite his magnificent work at Olympia, Phidias ran into trouble when he returned home. He was a close friend with Pericles, who ruled the Athens. Enemies of Pericles, unable to strike at the ruler directly, attacked his friends instead. Phidias was accused of stealing gold meant for the statue of Athena. When that charge failed to stick, they claimed he had carved his image, and that of Pericles into the sculpture found on the Parthenon. This would have been improper in the Greeks’ eyes and Phidias was thrown into jail where he died awaiting trial.
His masterpiece lived on, though, at the temple in Olympia until 392 A.D. when the Olympics were abolished by Emperor Theodosius I of Rome, a Christian who saw the games as a pagan rite. After that the statue was moved by wealthy Greeks to the city of Constantinople where it survived until destroyed by fire in 462 A.D..
The first archaeological work on the Olympia site was done by a group of French scientists in 1829. They were able to locate the outlines of the temple and found fragments of the sculpture showing the labors of Heracles. These pieces were shipped to Paris where they are still on display today at the Louvre.
The next expedition came from Germany in 1875 worked at Olympia for five summers. Over that period they were able to map out most of the buildings there, discovered more fragments of the temple’s sculpture, and located the remains of the pool in the floor that contained the oil for the statue.
In the 1950’s an excavation uncovered the workstop of Phidias which was discovered beneath an early Christain Church. Archaeologists found sculptor’s tools, a pit for casting bronze, clay molds, modeling plaster and even a portion of one of the elephant’s tusks which had supplied the ivory for the statue. Many of the clay molds, which had been used to shape the gold plates, bore serial numbers which must have been used to show the place of the plates in the design.
Today the stadium at the site has been restored. Little is left of the temple, though, except a few columns. Of the statue, which was perhaps the most wonderful work at Olympia, all is now gone.

==============================
The Temple of Artemis at Ephesus

A beautiful temple in Asia Minor erected in honor of the Greek goddess of hunting and wild nature
But when I saw the sacred house of Artemis that towers to the clouds, the [other Wonders] were placed in the shade, for the Sun himself has never looked upon its equal outside Olympus.
-- Antipater of Sidon
Is it simply a temple? How could it take its place among other unique structures such as the Pyramid, the Hanging Gardens, and the Colossus of Rhodes? For the people who actually visited it, the answer was simple. It was not just a temple... It was the most beautiful structure on earth... It was built in honor of the Greek goddess of hunting, wild nature, and fertility. That was the Temple of Artemis at Ephesus.
Location
The ancient city of Ephesus near the modern town of Selcuk, about 50 km south of Izmir (Smyrna) in Turkey.
History
Although the foundation of the temple dates back to the seventh century BC, the structure that earned a spot in the list of Wonders was built around 550 BC. Referred to as the great marble temple, or temple D, it was sponsored by the Lydian king Croesus and was designed by the Greek architect Chersiphron. The Temple was decorated with bronze statues sculpted by the most skilled artists of their time: Pheidias, Polycleitus, Kresilas, and Phradmon.
The temple served as both a marketplace and a religious institution. For years, the sanctuary was visited by merchants, tourists, artisans, and kings who paid homage to the goddess by sharing their profits with her. Recent archeological excavations at the site revealed gifts from pilgrims including statuettes of Artemis made of gold and ivory... earrings, bracelets, and necklaces... artifacts from as far as Persia and India.
On the night of 21 July 356 BC, a man named Herostratus burned the temple to ground in an attempt to immortalize his name, which he did indeed. Oddly enough, Alexander the Great was born the same night. The historian Plutarch later wrote that the goddess was “too busy taking care of the birth of Alexander to send help to her threatened temple”. And when Alexander the Great conquered Asia Minor, he offered to rebuild the destroyed temple, but the Temple was not restored until after his death in 323 BC. The temple was eventually restored and is labeled “Temple E” by archeologists.
When St Paul visited Ephesus to preach Christianity in the first century AD, he was confronted by the Artemis’ cult who had no plans to abandon their goddess. And when the temple was again destroyed by the Goths in AD 262, the Ephesians vowed to rebuild. By the fourth century AD, most Ephesians had converted to Christianity and the temple lost its religious glamor. The final chapter came when in AD 401 the Temple of Artemis was torn down by St John Chrysostom. Ephesus was later deserted, and only in the late nineteenth century has the site been excavated. The digging revealed the temple’s foundation and the road to the now swampy site. Attempts were recently made to rebuilt the temple, but only a few columns have been re-erected.
Description
The foundation of the temple was rectangular in form, similar to most temples at the time. Unlike other sanctuaries, however, the building was made of marble, with a decorated façade overlooking a spacious courtyard. Marble steps surrounding the building platform led to the high terrace which was approximately 80 m (260 ft) by 130 m (430 ft) in plan. The columns were 20 m (60 ft) high with Ionic capitals and carved circular sides. There were 127 columns in total, aligned orthogonally over the whole platform area, except for the central cella or house of the goddess.
The temple housed many works of art, including four ancient bronze statues of Amazons sculpted by the finest artists at the time. When St Paul visited the city, the temple was adorned with golden pillars and silver statuettes, and was decorated with paintings. There is no evidence that a statue of the goddess herself was placed at the center of the sanctuary, but there is no reason not to believe so.
The early detailed descriptions of the temple helped archeologists reconstruct the building. Many reconstructions such as that by H.F. von Erlach depicted the façade with a four-column porch which never existed. More accurate reconstructions may give us an idea about the general layout of the temple. However, its true beauty lies in the architectural and artistic details which will forever remain unknown.
-----------------
1100 A.D.: A troop of Crusaders stops at a muddy little village in Asia Minor. Their leader looks around. Confused ,he dismounts. This place is not what he expected. He read in the ancient texts that this was a large seaport with many ships docked in its bay. It isn’t. The sea is almost three miles away. The village is located in a swamp. There are no ships to be seen. The leader accosts a nearby man.
“Sir, is this the city of Ephesus?”
“It was called that once. Now it is named Ayasalouk.”
“Well, where is your bay? Where are the trading ships? And where is the magnificent Greek temple that we have heard about?”
Now it is the man’s turn to be confused. “Temple? What temple, Sir? We have no temple here...”
And so 800 years after its destruction, the magnificent Temple of Artemis at Ephesus, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, had been completely forgotten by the people of the town that had once held it in such pride.
And there is no doubt that the temple was indeed magnificent. “I have seen the walls and Hanging Gardens of ancient Babylon,” wrote Philon of Byzantium, “the statue of Olympian Zeus, the Colossus of Rhodes, the mighty work of the high Pyramids and the tomb of Mausolus. But when I saw the temple at Ephesus rising to the clouds, all these other wonders were put in the shade.”
So what happened to this great temple? And what happened to the city that hosted it? What turned Ephesus from a busy port of trade to a few shacks in a swamp?
The first shrine to the Goddess Artemis was probably built around 800 B.C. on a marshy strip near the river at Ephesus. The Ephesus Goddess Artemis, sometimes called Diana, is not the same figure as the Artemis worshiped in Greece. The Greek Artemis is the goddess of the hunt. The Ephesus Artemis was a goddess of fertility and was often pictured as draped with eggs, or multiple breasts, symbols of fertility, from her waist to her shoulders.
That earliest temple contained a sacred stone, probably a meteorite, that had “fallen from Jupiter.” The shrine was destroyed and rebuilt several times over the next few hundred years. By 600 B.C., the city of Ephesus had become a major port of trade and an architect named Chersiphron was engaged to build a new large temple. He designed it with high stone columns. Concerned that carts carrying the columns might get mired in the swampy ground around the site, Chersiphron laid the columns on their sides and had them rolled to where they would be erected.
This temple didn’t last long. In 550 B.C. King Croesus of Lydia conquered Ephesus and the other Greek cities of Asia Minor. During the fighting, the temple was destroyed. Croesus proved himself a gracious winner, though, by contributing generously to the building of a new temple.
This was next to the last of the great temples to Artemis in Ephesus and it dwarfed those that had come before. The architect is thought to be a man named Theodorus. Theodorus’s temple was 300 feet in length and 150 feet wide with an area four times the size of the temple before it. More than one hundred stone columns supported a massive roof. The new temple was the pride of Ephesus until 356 B.C. when a tragedy, by name of Herostratus, struck.
Herostratus was a young Ephesian who would stop at no cost to have his name go down in history. He managed this by burning the temple to the ground. The citizens of Ephesus were so appalled at this act they issued a decree that anyone who spoke of Herostratus would be put to death.
Shortly after this horrible deed, a new temple was commissioned. The architect was Scopas of Paros, one of the most famous sculptors of his day. Ephesus was one of the greatest cities in Asia Minor at this point and no expense was spared in the construction. According to Pliny the Elder, a Roman historian, the temple was a “wonderful monument of Grecian magnificence, and one that merits our genuine admiration.”
The temple was built in the same marshy place as before. To prepare the ground, Pliny recorded that “layers of trodden charcoal were placed beneath, with fleeces covered with wool upon the top of them.”
The building is thought to be the first completely constructed with marble and one of its must unusual features were 36 columns whose lower portions were carved with figures in high-relief (left). The temple also housed many works of art including four bronze statues of Amazon women.
Pliny recorded the length of this new temple at 425 feet and the width at 225 feet. Some 127 columns, 60 feet in height, supported the roof. In comparison the Parthenon, the remains of which stand on the acropolis in Athens today, was only 230 feet long, 100 feet wide and had 58 columns.
According to Pliny, construction took 120 years, though some experts suspect it may have only taken half that time. We do know that when Alexander the Great came to Ephesus in 333 B.C., the temple was still under construction. He offered to finance the completion of the temple if the city would credit him as the builder. The city fathers didn’t want Alexander’s name carved on the temple, but didn’t want to tell him that. They finally gave the tactful response: “It is not fitting that one god should build a temple for another god” and Alexander didn’t press the matter.
Pliny reported that earthen ramps were employed to get the heavy stone beams perched on top of the columns. This method seemed to work well until one of the largest beams was put into position above the door. It went down crookedly and the architect could find no way to get it to lie flat. He was beside himself with worry about this until he had a dream one night in which the Goddess herself appeared to him saying that he should not be concerned. She herself had moved the stone in the proper position. The next morning the architect found that the dream was true. During the night the beam had settled into its proper place.
The city continued to prosper over the next few hundred years and was the destination for many pilgrims coming to view the temple. A souvenir business in miniature Artemis idols, perhaps similar to a statue of her in the temple, grew up around the shrine. It was one of these business proprietors, a man named Demetrius, that gave St. Paul a difficult time when he visited the city in 57 A.D.
St. Paul came to the city to win converts to the then new religion of Christianity. He was so successful that Demetrius feared the people would turn away from Artemis and he would lose his livelihood. He called others of his trade together with him and gave a rousing speech ending with “Great is Artemis of the Ephesians!” They then seized two of Paul’s companions and a near riot followed. Eventually the city was quieted, the men released, and Paul left for Macedonia.
It was Paul’s Christianity that won out in the end, though. By the time the great Temple of Artemis was destroyed during a raid by the Goths in 262 A.D., both the city and the religion of Artemis were in decline. When the Roman Emperor Constantine rebuilt much of Ephesus a century later, he declined to restore the temple. He had become a Christian and had little interest in pagan temples.
Despite Constantine’s efforts, Ephesus declined in its importance as a crossroads of trade. The bay where ships docked disappeared as silt from the river filled it. In the end what was left of the city was miles from the sea, and many of the inhabitants left swampy lowland to live in the surrounding hills. Those that remained used the ruins of the temple as a source of building materials. Many of the fine sculptures were pounded into powder to make lime for wall plaster.
In 1863 the British Museum sent John Turtle Wood, an architect, to search for the temple. Wood met with many obstacles. The region was infested with bandits. Workers were hard to find. His budget was too small. Perhaps the biggest difficulty was that he had no idea where the temple was located. He searched for the temple for six years. Each year the British Museum threatened to cut off his funding unless he found something significant, and each year he convinced them to fund him for just one more season.
Wood kept returning to the site each year many despite hardships. During his first season he was thrown from a horse, breaking his collar bone. Two years later he was stabbed within an inch of his heart during an assassination attempt upon the British Consul in Smyrna.
Finally in 1869, at the bottom of a muddy twenty-foot deep test pit, his crew struck the base of the great temple. Wood then excavated the whole foundation removing 132,000 cubic yards of the swamp to leave a hole some 300 feet wide and 500 feet long. The remains of some of the sculptured portions were found and shipped the to British Museum where they can be viewed even today.
In 1904 another British Museum expedition under the leadership of D.G. Hograth continued the excavation. Hograth found evidence of five temples on the site, each constructed on top of the other.
Today the site of the temple is a marshy field. A single column is erect to remind visitors that once there stood in that place one of the wonders of the ancient world.

==============================
The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus

A fascinating tomb constructed for King Maussollos, Persian satrap of Caria
I have lying, over me in Halicarnassus, a gigantic monument such as no other dead person has, adorned in the finest way with statues of horses and men carved most realistically from the best quality marble.
-- King Maussollos in Lucian’s “Dialogues of the Dead”
Similar to the Great Pyramid, we are now visiting the burial place of an ancient king. Yet the Mausoleum is different - so different from the Pyramid that it earned its reputation - and a spot within the list - for other reasons. Geographically, it is closer to the Temple of Artemis... And it was the beauty of the tomb rather than its size that fascinated its visitors for years.
Location
In the city of Bodrum (f.k.a. Halicarnassus) on the Aegean Sea, in south-west Turkey.
History
When the Persians expanded their ancient kingdom to include Mesopotamia, Northern India, Syria, Egypt, and Asia Minor, the king could not control his vast empire without the help of local governors or rulers -- the Satraps. Like many other provinces, the kingdom of Caria in the western part of Asia Minor (Turkey) was so far from the Persian capital that it was practically autonomous. From 377 to 353 BC, king Mausollos of Caria reigned and moved his capital to Halicarnassus. Nothing is exciting about Maussollos life except the construction of his tomb. The project was conceived by his wife and sister Artemisia, and the construction might have started during the king’s lifetime. The Mausoleum was completed around 350 BC, three years after Maussollos death, and one year after Artemisia’s.
For 16 centuries, the Mausoleum remained in good condition until an earthquake caused some damage to the roof and colonnade. In the early fifteenth century, the Knights of St John of Malta invaded the region and built a massive crusader castle. When they decided to fortify it in 1494, they used the stones of the Mausoleum. By 1522, almost every block of the Mausoleum had been disassembled and used for construction.
Today, the massive castle still stands in Bodrum, and the polished stone and marble blocks of the Mausoleum can be spotted within the walls of the structure. Some of the sculptures survived and are today on display at the British Museum in London. These include fragment of statues and many slabs of the frieze showing the battle between the Greeks and the Amazons. At the site of the Mausoleum itself, only the foundation remains of the once magnificent Wonder.
Description
The structure was rectangular in plan, with base dimensions of about 40 m (120 ft) by 30 m (100 ft). Overlying the foundation was a stepped podium which sides were decorated with statues. The burial chamber and the sarcophagus of white alabaster decorated with gold were located on the podium and surrounded by Ionic columns. The colonnade supported a pyramid roof which was in turn decorated with statues. A statue of a chariot pulled by four horses adorned the top of the tomb.
The total height of the Mausoleum was 45 m (140 ft). This is broken down into 20 m (60 ft) for the stepped podium, 12 m (38 ft) for the colonnade, 7 m (22 ft) for the pyramid, and 6 m (20 ft) for the chariot statue at the top.
The beauty of the Mausoleum is not only in the structure itself, but in the decorations and statues that adorned the outside at different levels on the podium and the roof. These were tens of life-size as well as under and over life-size free-standing statues of people, lions, horses, and other animals. The statues were carved by four Greek sculptors: Bryaxis, Leochares, Scopas, and Timotheus, each responsible for one side. Because the statues were of people and animals, the Mausoleum holds a special place in history as it was not dedicated to the gods of Ancient Greece.
Since the nineteenth century, archeological excavations have been undertaken at the Mausoleum site. These excavations together with detailed descriptions by ancient historians give us a fairly good idea about the shape and appearance of the Mausoleum. A modern reconstruction of the shorter side of the Mausoleum illustrates the lavish nature of the art and architecture of the building... a building for a King whose name is celebrated in all large tombs today -- mausoleums.
---------------------
In 377 B.C., the city of Halicarnassus was the capitol of a small kingdom along the Mediterranean coast of Asia Minor. It was in that year the ruler of this land, Hecatomnus of Mylasa, died and left control of the kingdom to his son, Mausolus. Hecatomnus, a local satrap to the Persians, had been ambitious and had taken control of several of the neighboring cities and districts. Mausolus in his time, extended the territory even further so that it finally included most of southwestern Asia Minor.
Mausolus, with his queen Artemisia, ruled over Halicarnassus and the surrounding territory for 24 years. Mausolus, though he was descended from the local people, spoke Greek and admired the Greek way of life and government. He founded many cities of Greek design along the coast and encouraged Greek democratic traditions.
Then in 353 B.C. Mausolus died, leaving his queen Artemisia, who was also his sister (It was the custom in Caria for rulers to marry their own sisters), broken-hearted. As a tribute to him, she decided to build him the most splendid tomb in the known world. It became a structure so famous that Mausolus’s name is now associated with all stately tombs through our modern word mausoleum. The building was also so beautiful and unique it became one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
Artemisia decided that no expense was to be spared in the building of the tomb. She sent messengers to Greece to find the most talented artists of the time. This included Scopas, the man who had supervised the rebuilding of the Temple to Artemis at Ephesus. Other famous sculptors such as Bryaxis, Leochares and Timotheus joined him as well as hundreds of other craftsmen.
The tomb was erected on a hill overlooking the city. The whole structure sat in an enclosed courtyard. At the center of the courtyard was a stone platform on which the tomb itself sat. A staircase, flanked by stone lions, led to the top of this platform. Along the outer wall of this were many statues depicting gods and goddess. At each corner stone warriors, mounted on horseback, guarded the tomb.
At the center of the platform was the tomb itself. Made mostly of marble, the structure rose as a square, tapering block to about one-third of the Mausoleum’s 140 foot height. This section was covered with relief sculpture showing action scenes from Greek myth/history. One part showed the battle of the Centaurs with the Lapiths. Another depicted Greeks in combat with the Amazons, a race of warrior women.
On top of this section of the tomb thirty-six slim columns, nine per side, rose for another third of the height. Standing in between each column was another statue. Behind the columns was a solid block that carried the weight of the tomb’s massive roof.
The roof, which comprised most of the final third of the height, was in the form of a stepped pyramid. Perched on top was the tomb’s penultimate work of sculpture: Four massive horses pulling a chariot in which images of Mausolus and Artemisia rode.
Soon after construction of the tomb started Artemisia found herself in a crisis. Rhodes, an island in the Aegean Sea between Greece and Asia Minor, had been conquered by Mausolus. When the Rhodians heard of his death they rebelled and sent a fleet of ships to capture the city of Halicarnassus. Knowing that the Rhodian fleet was on the way, Artemisa hid her own ships at a secret location at the east end of the city’s harbor. After troops from the Rhodian fleet disembarked to attack, Artemisia’s fleet made a surprise raid, captured the Rhodian fleet, and towed it out to sea.
Artemisa put her own soldiers on the invading ships and sailed them back to Rhodes. Fooled into thinking that the returning ships were their own victorious navy, the Rhodians failed to put up a defense and the city was easily captured quelling the rebellion.
Artemisa lived for only two years after the death of her husband. Both would be buried in the yet unfinished tomb. According to the historian Pliny, the craftsmen decided to stay and finish the work after their patron died “considering that it was at once a memorial of their own fame and of the sculptor’s art.”
The Mausoleum overlooked the city of Halicarnassus for many centuries. It was untouched when the city fell to Alexander the Great in 334 B.C. and still undamaged after attacks by pirates in 62 and 58 B.C.. It stood above the city ruins for some 17 centuries. Then a series of earthquakes shattered the columns and sent the stone chariot crashing to the ground. By 1404 A.D. only the very base of the Mausoleum was still recognizable.
Crusaders, who had occupied the city from the thirteen century onward, recycled the broken stone into their own buildings. In 1522 rumors of a Turkish invasion caused Crusaders to strengthen the castle at Halicarnassus (which was by then known as Bodrum) and much of the remaining portions of the tomb was broken up and used within the castle walls. Indeed sections of polished marble from the tomb can still be seen there today.
At this time a party of knights entered the base of the monument and discovered the room containing a great coffin. The party, deciding it was too late to open it that day, returned the next morning to find the tomb, and any treasure it may have contained, plundered. The bodies of Mausolus and Artemisia were missing too. The Knights claimed that Moslem villagers were responsible for the theft, but it is more likely that some of the Crusaders themselves plundered the graves.
Before grounding much of the remaining sculpture of the Mausoleum into lime for plaster the Knights removed several of the best works and mounted them in the Bodrum castle. There they stayed for three centuries. At that time the British ambassador obtained several of the statutes from the castle, which now reside in the British Museum.
In 1846 the Museum sent the archaeologist Charles Thomas Newton to search for more remains of the Mausoleum. He had a difficult job. He didn’t know the exact location of the tomb and the cost of buying up all the small parcels of land in the area to look for it would have been astronomical. Instead Newton studied the accounts of ancient writers like Pliny to obtain the approximate size and location of the memorial, then bought a plot of land in the most likely location. Digging down, Newton explored the surrounding area through tunnels he dug under the surrounding plots. He was able to locate some walls, a staircase, and finally three of the corners of the foundation. With this knowledge, Newton was able to figure out which plots of land he needed to buy.
Newton then excavated the site and found sections of the reliefs that decorated the wall of the building and portions of the stepped roof. Also a broken stone chariot wheel, some seven feet in diameter, from the sculpture on the roof was discovered. Finally, he found the statues of Mausolus and Artemisia that had stood at the pinnacle of the building.
Today these works of art stand in the Mausoleum Room at the British Museum. There the images of Mausolus and his queen forever watch over the few broken remains of the beautiful tomb she built for him.

==============================
The Colossus of Rhodes

A colossus of Helios the sun-god, erected by the Greeks near the harbor of a Mediterranean Island
To you, O Sun, the people of Dorian Rhodes set up this bronze statue reaching to Olympus when they had pacified the waves of war and crowned their city with the spoils taken from the enemy. Not only over the seas but also on land did they kindle the lovely torch of freedom.
-- Dedicatory inscription of the Colossus
From its building to its destruction lies a time span of merely 56 years. Yet the colossus earned a place in the famous list of Wonders. “But even lying on the ground, it is a marvel”, said Pliny the Elder. The Colossus of Rhodes was not only a gigantic statue. It was rather a symbol of unity of the people who inhabited that beautiful Mediterranean island -- Rhodes.
Location
At the entrance of the harbor of the Mediterranean island of Rhodes in Greece.
History
Throughout most of its history, ancient Greece was comprised of city-states which had limited power beyond their boundary. On the small island of Rhodes were three of these: Ialysos, Kamiros, and Lindos. In 408 BC, the cities united to form one territory, with a unified capital, Rhodes. The city thrived commercially and had strong economic ties with their main ally, Ptolemy I Soter of Egypt. In 305 BC, the Antigonids of Macedonia who were also rivals of the Ptolemies, besieged Rhodes in an attempt to break the Rhodo-Egyptian alliance. They could never penetrate the city. When a peace agreement was reached in 304 BC, the Antagonids lifted the siege, leaving a wealth of military equipment behind. To celebrate their unity, the Rhodians sold the equipment and used the money to erect an enormous statue of their sun god, Helios.
The construction of the Colossus took 12 years and was finished in 282 BC. For years, the statue stood at the harbor entrance, until a strong earthquake hit Rhodes about 226 BC. The city was badly damaged, and the Colossus was broken at its weakest point -- the knee. The Rhodians received an immediate offer from Ptolemy III Eurgetes of Egypt to cover all restoration costs for the toppled monument. However, an oracle was consulted and forbade the re-erection. Ptolemy’s offer was declined.
For almost a millennium, the statue lay broken in ruins. In AD 654, the Arabs invaded Rhodes. They disassembled the remains of the broken Colossus and sold them to a Jew from Syria. It is said that the fragments had to be transported to Syria on the backs of 900 camels.
Description
Let us first clear a misconception about the appearance of the Colossus. It has long been believed that the Colossus stood in front of the Mandraki harbor, one of many in the city of Rhodes, straddling its entrance. Given the height of the statue and the width of the harbor mouth, this picture is rather impossible than improbable. Moreover, the fallen Colossus would have blocked the harbor entrance. Recent studies suggest that it was erected either on the eastern promontory of the Mandraki harbor, or even further inland. Anyway, it did never straddle the harbor entrance.
The project was commissioned by the Rhodian sculptor Chares of Lindos. To build the statue, his workers cast the outer bronze skin parts. The base was made of white marble, and the feet and ankle of the statue were first fixed. The structure was gradually erected as the bronze form was fortified with an iron and stone framework. To reach the higher parts, an earth ramp was built around the statue and was later removed. When the colossus was finished, it stood about 33 m (110 ft) high. And when it fell, “few people can make their arms meet round the thumb”, wrote Pliny.
Although we do not know the true shape and appearance of the Colossus, modern reconstructions with the statue standing upright are more accurate than older drawings. Although it disappeared from existence, the ancient World Wonder inspired modern artists such as French sculptor Auguste Bartholdi best known by his famous work: The Statue of Liberty.
---------------------
Travelers to New York City harbor see a marvelous sight. Standing on a small island in the harbor is an immense statue of a robed woman, holding a book and lifting a torch to the sky. The statue measures almost one-hundred and twenty feet from foot to crown. It is sometimes referred to as the “Modern Colossus,” but more often called the Statue of Liberty.
This awe-inspiring statue was a gift from France to America and is easily recognized by people around the world. What many visitors to this shrine to freedom don’t know is that the statue, the “Modern Colossus,” is the echo of another statue, the original colossus that stood over two thousand years ago at the entrance to another busy harbor on the Island of Rhodes. Like the Statue of Liberty, this colossus was also built as a celebration of freedom. This amazing statue, standing the same height from toe to head as the modern colossus, was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
The island of Rhodes was an important economic center in the ancient world. It is located off the southwestern tip of Asia Minor where the Aegean Sea meets the Mediterranean. The capitol city, also named Rhodes, was built in 408 B.C. and was designed to take advantage of the island’s best natural harbor on the northern coast.
In 357 B.C. the island was conquered by Mausolus of Halicarnassus (whose tomb is one of the other Seven Wonders of the Ancient World), fell into Persian hands in 340 B.C., and was finally captured by Alexander the Great in 332 B.C.. When Alexander died of a fever at an early age, his generals fought bitterly among themselves for control of Alexander’s vast kingdom. Three of them, Ptolemy, Seleucus, and Antigous, succeeded in dividing the kingdom among themselves.
The Rhodians supported Ptolemy (who wound up ruling Egypt) in this struggle. This angered Antigous who sent his son Demetrius to capture and punish the city of Rhodes.
The war was long and painful. Demetrius brought an army of 40,000 men. This was more than the entire population of Rhodes. He also augmented his force by using Aegean pirates.
The city was protected by a strong, tall, wall and the attackers were forced to use siege towers to try and climb over it. Siege towers were wooden structures often armed with catapults that could be moved up to a defender’s walls to allow the attackers to scale them. While some were designed to be rolled up on land, Demetrius used a giant tower mounted on top of six ships lashed together to make his attack. This tower, though, was turned over and smashed when a storm suddenly approached. The battle was won by the Rhodians.
Demetrius had a second supertower built. This one stood almost 150 feet high and some 75 feet square at the base. It was equipped with many catapults and skinned with wood and leather to protect the troops inside from archers. It even carried water tanks that could be used to fight fires started by flaming arrows. This tower was mounted on iron wheels and could be rolled up to the walls.
When Demetrius attacked the city, the defenders stopped the war machine by flooding a ditch outside the walls and miring the heavy monster in the mud. By then almost a year had gone by and a fleet of ships from Egypt arrived to assist the city. Demetrius withdrew quickly leaving the great siege tower where it was.
To celebrate their victory and freedom, the Rhodians decided to build a giant statue of their patron god Helios. They melted down bronze from the many war machines Demetrius left behind for the exterior of the figure and the super siege tower became the scaffolding for the project. According to Pliny, a historian who lived several centuries after the Colossus was built, construction took 12 years. Other historians place the start of the work in 304 B.C..
The statue was one hundred and ten feet high and stood upon a fifty-foot pedestal near the harbor mole. Although the statue has been popularly depicted with its legs spanning the harbor entrance so that ships could pass beneath, it was actually posed in a more traditional Greek manner: nude, wearing a spiked crown, shading its eyes from the rising sun with its right hand, while holding a cloak over its left.
No ancient account mentions the harbor-spanning pose and it seems unlikely the Greeks would have depicted one of their gods in such an awkward manner. In addition, such a pose would mean shutting down the harbor during the construction, something not economically feasible.
The statue was constructed of bronze plates over an iron framework (very similar to the Statue of Liberty which is copper over a steel frame). According to the book of Pilon of Byzantium, 15 tons of bronze were used and 9 tons of iron, though these numbers seem low. The Statue of Liberty, roughly of the same size, weighs 225 tons. The Colossus, which relied on weaker materials, must have weighed at least as much and probably more.
Ancient accounts tell us that inside the statue were several stone columns which acted as the main support. Iron beams were driven into the stone and connected with the bronze outer skin. Each bronze plate had to be carefully cast then hammered into the right shape for its location in the figure, then hoisted into position and riveted to the surrounding plates and the iron frame.
The architect of this great construction was Chares of Lindos, a Rhodian sculptor who was a patriot and fought in defense of the city. Chares had been involved with large scale statues before. His teacher, Lysippus, had constructed a 60-foot high likeness of Zeus. Chares probably started by making smaller versions of the statue, maybe three feet high, then used these as a guide to shaping each of the bronze plates of the skin.
It is believed Chares did not live to see his project finished. There are several legends that he committed suicide. In one tale he has almost finished the statue when someone points out a small flaw in the construction. The sculptor is so ashamed of it he kills himself.
In another version the city fathers decide to double the height of the statue. Chares only doubles his fee, forgetting that doubling the height will mean an eightfold increase in the amount of materials needed. This drives him into bankruptcy and suicide.
There is no evidence that either of these tales are true.
The Colossus stood proudly at the harbor entrance for some fifty-six years. Each morning the sun must have caught its polished bronze surface and made the god’s figure shine. Then an earthquake hit Rhodes and the statue collapsed. Huge pieces of the figure lay along the harbor for centuries.
“Even as it lies,” wrote Pliny, “it excites our wonder and admiration. Few men can clasp the thumb in their arms, and its fingers are larger than most statues. Where the limbs are broken asunder, vast caverns are seen yawning in the interior. Within it, too, are to be seen large masses of rock, by the weight of which the artist steadied it while erecting it.”
It is said that an Egyptian king offered to pay for its reconstruction, but the Rhodians refused. They feared that somehow the statue had offended the god Helios, who used the earthquake to throw it down.
In the seventh century A.D. the Arabs conquered Rhodes and broke the remains of the Colossus up into smaller pieces and sold it as scrap metal. Legend says it took 900 camels to carry away the statue. A sad end for what must have been a majestic work of art.
==============================
The Lighthouse of Alexandria

A lighthouse built by the Ptolemies on the island of Pharos off the coast of their capital city
Sostratus, the son of Dexiphanes, the Cnidian, dedicated this to the Saviour Gods, on behalf of those who sail the seas.
-- Dedicatory inscription of the Lighthouse
Of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, only one had a practical use in addition to its architectural elegance: The Lighthouse of Alexandria. For sailors, it ensured a safe return to the Great Harbor. For architects, it meant even more: it was the tallest building on Earth. And for scientists, it was the mysterious mirror that fascinated them most... The mirror which reflection could be seen more than 50 km (35 miles) off-shore.
Location
On the ancient island of Pharos, now a promontory within the city of Alexandria in Egypt.
History
Shortly after the death of Alexander the Great, his commander Ptolemy Soter assumed power in Egypt. He had witnessed the founding of Alexandria, and established his capital there. Off of the city’s coast lies a small island: Pharos. Its name, legend says, is a variation of Pharaoh’s Island, but it is more likely that the name is Greek in origin. The island was connected to the mainland by means of a dike - the Heptastadion - which gave the city a double harbor. And because of dangerous sailing conditions and flat coastline in the region, the construction of a lighthouse was necessary.
The project was conceived and initiated by Ptolemy Soter around 290 BC, but was completed after his death, during the reign of his son Ptolemy Philadelphus. Sostratus, a contemporary of Euclid, was the architect, but detailed calculations for the structure and its accessories were carried out at the Alexandria Library/Mouseion. The monument was dedicated to the Savior Gods: Ptolemy Soter (lit. savior) and his wife Berenice. For centuries, the Lighthouse of Alexandria (occasionally referred to as the Pharos Lighthouse) was used to mark the harbor, using fire at night and reflecting sun rays during the day. It was even shown on Roman coins, just as famous monuments are depicted on currency today.
When the Arabs conquered Egypt, they admired Alexandria and its wealth. The Lighthouse continues to be mentioned in their writings and travelers accounts. But the new rulers moved their capital to Cairo since they had no ties to the Mediterranean. When the mirror was brought down mistakenly, they did not restore it back into place. In AD 956, an earthquake shook Alexandria, and caused little damage to the Lighthouse. It was later in 1303 and in 1323 that two stronger earthquakes left a significant impression on the structure. When the famous Arab traveler Ibn Battuta visited Alexandria in 1349, he could not enter the ruinous monument or even climb to its doorway.
The final chapter in the history of the Lighthouse came in AD 1480 when the Egyptian Mamelouk Sultan, Qaitbay, decided to fortify Alexandria’s defense. He built a medieval fort on the same spot where the Lighthouse once stood, using the fallen stone and marble.
Description
Of the six vanished Wonders, the Lighthouse of Alexandria was the last to disappear. Therefore we have adequately accurate knowledge of its location and appearance. Ancient accounts such as those by Strabo and Pliny the Elder give us a brief description of the “tower” and the magnificent white marble cover. They tell us how the mysterious mirror could reflect the light tens of kilometers away. Legend says the mirror was also used to detect and burn enemy ships before they could reach the shore.
In 1166, an Arab traveler, Abou-Haggag Al-Andaloussi visited the Lighthouse. He documented a wealth of information and gave an accurate description of the structure which helped modern archeologists reconstruct the monument. It was composed of three stages: The lowest square, 55.9 m (183.4 ft) high with a cylindrical core; the middle octagonal with a side length of 18.30 m (60.0 ft) and a height of 27.45 m (90.1 ft); and the third circular 7.30 m (24.0 ft) high. The total height of the building including the foundation base was about 117 m (384 ft), equivalent to a 40-story modern building. The internal core was used as a shaft to lift the fuel needed for the fire. At the top stage, the mirror reflected sunlight during the day while fire was used during the night. In ancient times, a statue of Poseidon adorned the summit of the building.
Although the Lighthouse of Alexandria did not survive to the present day, it left its influence in various respects. From an architectural standpoint, the monument has been used as a model for many prototypes along the Mediterranean, as far away as Spain. And from a linguistic standpoint, it gave its name -- Pharos -- to all the lighthouses in the world... Just look up the dictionary for the French, Italian, or Spanish word for lighthouse.
-----------------
In the fall of 1994 a team of archaeological scuba divers entered the waters off of Alexandria, Egypt. Working beneath the surface they searched the bottom of the sea for artifacts. Large underwater blocks of stone were marked with floating masts so that an Electronic Distance Measurement station on shore could obtain their exact positions. Global positioning satellites were used to further fix the locations. The information was then fed into computers to create a detailed database of the sea floor.
Ironically, these scientists were using some of the most high-tech devices available at the end of the 20th century to try and discover the ruins of one of the most advanced technological achievements of the 3rd century, B.C.: The Pharos. It was the great lighthouse of Alexandria, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
The story of the Pharos starts with the founding of the city of Alexandria by the Macedonian conqueror Alexander the Great in 332 B.C.. Alexander started at least 17 cities named Alexandria at different locations in his vast domain. Most of them disappeared, but Alexandria in Egypt thrived for centuries and continues even today.
Alexander the Great choose the location of his new city carefully. Instead of building it on the Nile delta, he selected a site some twenty miles to the west, so that the silt and mud carried by the river would not block the city harbor. South of the city was the marshy Lake Mareotis. After a canal was constructed between the lake and the Nile, the city had two harbors: one for Nile River traffic, and the other for Mediterranean Sea trade. Both harbors would remain deep and clear.
Alexander died soon after in 323 B.C. and the city was completed by Ptolemy Soter the new ruler of Egypt. Under Ptolemy the city became rich and prosperous. However, it needed both a symbol and a mechanism to guide the many trade ships into the busy harbor. Ptolemy authorized the building of the Pharos in 290 B.C., and when it was completed some twenty years later, it was the first lighthouse in the world and the tallest building in existence, with the exception of the Great Pyramid.
The lighthouse’s designer was Sostrates of Knidos. Proud of his work, Sostrates, desired to have his name carved into the foundation. Ptolemy II, the son who ruled Egypt after his father, refused this request wanting his own name to be the only one on the building. A clever man, Sostrates had the inscription:
SOSTRATES SON OF DEXIPHANES OF KNIDOS ON BEHALF OF ALL MARINERS TO THE SAVIOR GODS
chiseled into the foundation, then covered it with plaster. Into the plaster was chiseled Ptolemy’s name. As the years went by the plaster aged and chipped away revealing Sostrates’ declaration.
The lighthouse was built on the island of Pharos and soon the building itself acquired the name. The connection of the name with the function became so strong that the word “Pharos” became the root of the word “lighthouse” in the French, Italian, Spanish and Romanian languages.
There are two detailed descriptions made of the lighthouse in the 10th century A.D. by Moorish travelers Idrisi and Yusuf Ibn al-Shaikh. According to their accounts, the building was 300 cubits high. Because the cubit measurement varied from place to place, this could mean that the Pharos stood anywhere from 450 to 600 feet in height, although the lower figure is more likely.
The design was unlike the slim single column of most modern lighthouses (left), but more like the structure of an early twentieth century skyscraper. There were three stages, each built on top of the lower. The building was constructed of marble blocks with lead mortar. The lowest level was probably more that 200 feet in height and 100 feet square, shaped like a massive box. Inside this section was a large spiral ramp that allowed materials to be pulled to the top in horse-drawn carts.
On top of this section was an eight-sided tower. On top of the tower was a cylinder that extended up to an open cupola where the fire that provided the light burned. On the roof of the cupola was a large statue of Poseidon. The lower portion of the building contained hundreds of storage rooms.
The interior of the upper two sections had a shaft with a dumbwaiter that was used to transport fuel up to the fire. Staircases allowed visitors and the keepers to climb to the beacon chamber. There, according to reports, a large curved mirror, perhaps made of polished metal, was used to project the fire’s light into a beam. It was said ships could detect the light from the tower at night or the smoke from the fire during the day up to one-hundred miles away.
There are stories that this mirror could be used as a weapon to concentrate the sun and set enemy ships ablaze as they approached. Another tale says that it was possible to use the mirror to magnify the image of the city of Constantinople from far across the sea to observe what was going on there. Both of these stories seem implausible, though.
The lighthouse was apparently a tourist attraction. Food was sold to visitors at the observation platform at the top of the first level. A smaller balcony provided a view from the top of the eight-sided tower for those that wanted to make the additional climb. The view from there must have been impressive as it was probably 300 feet above the sea. There were few places in the ancient world where a person could ascend a man-made tower to get such a perspective.
How then did the world’s first lighthouse wind up on the floor of the Mediterranean Sea? Most accounts indicate that it, like many other ancient buildings, was the victim of earthquakes. It stood for 1,500 years but was damaged by tremors in 365 and 1303 A.D. Reports indicate the final collapse came in 1326.
There is also an unlikely tale that part of the lighthouse was demolished through trickery. In 850 A.D. the Emperor of Constantinople, a rival port, devised a clever plot to get rid of the Pharos. He spread rumors that buried under the lighthouse was a fabulous treasure. When the Caliph at Cairo who controlled Alexandria heard these rumors, he ordered that the tower be pulled down to get at the treasure. It was only after the great mirror had been destroyed and the top two portions of the tower removed that the Caliph realized he’d been deceived. He tried to rebuild the tower, but couldn’t, so he turned it into a mosque instead.
As colorful as this story is there does not seem to be much truth in it. Visitors in 1115 A.D. reported the Pharos intact and still operating as a lighthouse.
Did the divers actually find the remains of Pharos in the bottom of the harbor? Some of the larger blocks of stone found certainly seem to have come from a large building. Statues were located that may have stood at the base of the Pharos. Interestingly enough, much of the material found seems to be from earlier eras than the lighthouse. Scientists speculate that they may have been recycled in the construction of the Pharos from even older buildings.
There are plans to turn this site into an archaeological park with a lighthouse museum. In a few years visitors maybe able to rent snorkle gear and wet suits and dive in the bay among the remains of the great Pharos lighthouse.

==============================
Other Wonders
Sights seen in the mind’s eye can never be destroyed
-- Strabo (64 BC - AD 21)
Six out of seven Ancient Wonders did not survive to this present day. Human imagination urged poets, writers, and historians to seek “replacements” for the fallen monuments. Some proposed a new list for the Seven Wonders of the Modern World. Others argued that Ancient civilizations which the Greeks did not know of, erected monuments that should have been included in the original list. Wonders such as the Great Wall of China, Taj Mahal in Agra, and the Temple of Angkor in Cambodia are a few examples.
Like the ancient list, the new ones include fascinating monuments and structures that changed the existing landscape. However, no single list won unanimous approval among historians, artists, and architects. Here is an alphabetical listing of some Forgotten, Modern, and Natural Wonders.
Forgotten Wonders
* Abu Simbel Temple in Egypt
* Angkor Wat in Cambodia
* The Aztec Temple in Tenochtitlan (Mexico City), Mexico
* The Banaue Rice Terraces in the Philippines
* Borobudur Temple in Indonesia
* The Colosseum in Rome, Italy
* The Great Wall of China
* The Inca city of Machu Picchu, Peru
* The Leaning Tower of Pisa, Italy
* The Mayan Temples of Tikal in Northern Guatemala
* The Moai Statues in Rapa Nui (Easter Island), Chile
* Mont-Saint-Michel in Normandy, France
* The Throne Hall of Persepolis in Iran
* The Parthenon in Athens, Greece
* Petra, the rock-carved city in Jordan
* The Shwedagon Pagoda in Myanmar
* Stonehenge in England
* Taj Mahal in Agra, India
* The Temple of the Inscriptions in Palenque, Mexico
Modern Wonders
* The Channel Tunnel
* The Clock Tower (Big Ben) in London, England
* The CN Tower in Toronto, Canada
* Eiffel Tower in Paris, France
* The Empire State Building in New York City, USA
* The Gateway Arch in St. Louis, USA
* The Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco, USA
* The High Dam in Aswan, Egypt
* Hoover Dam in Arizona/Nevada, USA
* Itaipú Dam in Brazil/Paraguay
* Mount Rushmore National Memorial in South Dakota, USA
* The Panama Canal
* The Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
* The Statue of Cristo Redentor in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
* The Statue of Liberty in New York City, USA
* The Suez Canal in Egypt
* The Sydney Opera House in Australia
Natural Wonders
* Angel Falls in Venezuela
* The Bay of Fundy in Nova Scotia, Canada
* The Grand Canyon in Arizona, USA
* The Great Barrier Reef in Australia
* Iguaçú Falls in Brazil/Argentina
* Krakatoa Island in Indonesia
* Mount Everest in Nepal
* Mount Fuji in Japan
* Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania
* Niagara Falls in Ontario (Canada) and New York State (USA)
* Paricutin Volcano in Mexico
* Victoria Falls in Zambia/Zimbabwe
==============================
The Tower of Babel

Now the whole earth had one language and few words. And as men migrated from the east, they found a plain in the land of Shinar and settled there. And they said to one another, “Come, let us make bricks, and burn them thoroughly.” And they had brick for stone, and bitumen for mortar. Then they said, “Come, let us build ourselves a city, and a tower with its top in the heavens, and let us make a name for ourselves, lest we be scattered abroad upon the face of the whole earth.”
And the Lord came down to see the city and the tower, which the sons of men had built. And the Lord said, “Behold, they are one people, and they have all one language; and this is only the beginning of what they will do; and nothing that they propose to do will now be impossible for them. Come, let us go down, and there confuse their language, that they may not understand one another’s speech.”
So the Lord scattered them abroad from there over the face of the earth, and they left off building the city. Therefore its name was called Babel, because there the Lord confused the language of all the earth; and from there the Lord scattered them abroad over the face of the earth. - Genesis 11.
The story of the tower of Babel found in the Bible is familiar to many. Is there evidence that such a tower really existed? There are archaeological indications that it did, indeed.
In the fertile Mesopotamian plain between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, in what is now modern Iraq, is a mound, or tell, of broken mud-brick buildings and debris. This is all that remains of the ancient famed city of Babylon.
Babylon was one of a number of cities built by a succession of peoples that lived on the plain starting around 5,500 years ago. There developed a tradition in each city of building a temple in the shape of a stepped pyramid. These temples, or ziggurates, most likely honored a particular god. The people of Mesopotamia believed in many gods and often a city might have several ziggurates. Over time Babylon became the most influential city on the plain and its ziggurat, honoring the god Marduk, was built, destroyed and rebuilt until it was the tallest tower.
Archaeologists examining the remains of the city of Babylon have found what appears to be the foundation of the tower: a square of earthen embankments some three-hundred feet on each side. The tower’s most splendid incarnation was probably under King Nebuchadnezzar II who lived from 605-562 BC. The King rebuilt the tower to stand 295 feet high. According to an inscription made by the king the tower was constructed of “baked brick enameled in brilliant blue.” The terraces of the tower may have also been planted with flowers and trees.
Constructing ziggurats on the Mesopotamian plain was not easy. The area lacks the stone deposits the Egyptians used effectively for their timeless monuments. The wood available is mostly palm, not the best for construction, so the people used what they had in abundance: mud and straw. The bulk of the towers were constructed of crude bricks made by mixing chopped straw with clay and pouring the results into molds. After the bricks were allowed to bake in the sun they were joined in construction by using bitumen, a slimey material imported from the Iranian plateau. Bitumen was used widely as a binding and coating material throughout the Mesopotamian plain.
The tower, referred to by the Babylonians as Etemenanki, was only one of the marvels of the city. Down the street was the Hanging Gardens, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Nebuchadnezzar also had two impressive palaces inside the city. The final beginning of the end of the tower of Babel probably began around 478 BC. The city had been taken over by the Persian King Xerxes who crushed a rebellion there that year. The tower was neglected and crumbled .
Because of the use of mud-baked bricks, ziggurats needed constant maintenance. Often they had elaborate internal drainage systems to channel rain water away so that the bricks would not be eroded. If the pipes on a ziggurat were not cleaned regularly and allowed to jam the tower would slowly crumble. Ziggurats were also highly susceptible to earthquake damage. Their height amplified the effect of quake forces while the rigid, unreinforced-brick construction did not allow the structures to flex with the shaking.
Although the Tower of Babel now gone, a few lessor ziggurats still exist. The largest surviving, (although damaged) temple is now found in western Iran, in what was once the ancient land of Elam. It is located about 18 miles from the capital of Elam, a city named Susa. Built in 1250 BC by the King Untash-Napirisha it once had five levels and stood 170 feet in height.
What we know about the Tower of Babel today comes only from the little archaeological evidence found and a few ancient writings. Nebuchadnezzar described how “gold, silver and precious stones from the mountain and from the sea were liberally set into the foundations” and how to rebuild it he called on “various peoples of the Empire, from north and south, from mountains and the coasts” to help with the construction.
Even in 460 BC, after the tower had been crumbling for many years, the Greek historian Herodotus visited the tower and was very impressed. “It has a solid central tower, one furlong square, with a second erected on top of it and then a third, and so on up to eight. All eight towers can be climbed by a spiral way running around the outside, and about halfway up there are seats for those who make the journey to rest on.”
Though the tower has been gone for many years, its biblical story has continued to inspire artists. It was a favorite subject during the 14th century when several well-known paintings were done. As archaeological and historical research has shown most were not truly representative of the actual building.
==============================
Stonehenge and the Rings of Rock


Stonehenge maybe, in many peoples’ minds, the most mysterious place in the world. This set of concentric rings and horseshoe shapes on the empty Salisbury Plain, is, at the age of 4,000 years, one of the oldest, and certainly best preserved, megalithic (that means large, often ancient, stone) structures on Earth. It is a fantastic construction with many of the larger stones involved weighing 25 tons and quarried from a location 18 miles away. The rings and horseshoes of Sarsen (a type of sandstone) also carry massive lintels connecting them so that when they were all in place there was a ring of stone in the sky as well as on the ground.
We know almost nothing about who built Stonehenge and why. A popular theory advanced in the 19th century was that the Druids, a people that existed in Britain before the Roman conquest, had built it as a temple. Modern archaeological techniques, though, have dated Stonehenge and we now know that it was completed at least a 1,000 years before the Druids came to power. If Druids used Stonehenge for their ceremonies they got the site secondhand. Despite this, modern Druids have laid claim to Stonehenge and an annual ceremony takes place at Stonehenge during Summer solstice, one of the ring’s astronomical alignments.
There is evidence there was activity on the Stonehenge site as far back as 11,000 years ago. It wasn’t until about 3100 BC, though, that a circular bank, following the current Stonehenge layout, appeared. At the same time pine posts were put into place. Around 2100 BC stones started being erected. First bluestones from Wales, then the larger Sarsens stones. During this period some stones were erected, then later dismantled.
Why did the builders create, dismantle and rebuild this isolated site? It’s hard to say. They apparently didn’t have a written language and left no records. We can say one thing about Stonehenge based on archaeological digs at the location. There is almost no “trash.” A number of pieces of flint, antler picks or axes have been found, but very few items that one would expect to see discarded at a human habitation (Trash pits turn out to be some of the best sources of material for archaeologists to examine). This leads some archaeologists to conclude that Stonehenge was “sacred ground,” like a church. As one scientist put it Stonehenge was a “clearly special place were you didn’t drop litter.”
Stonehenge at about 1500 BC consisted of a circular ditch, with a raised bank on the inside. Within the bank was a circle of 30 Sarsen stones with lintels creating a raised circle. Today only 17 of those stones still stand and few of the lintels are still in position. Within the ring were five “trilithons” (two massive upright stones supporting a lintel) arranged in a horseshoe. On the open side of the horseshoe, outside the ditch, was the heel stone, some 120 feet from the ring. Once a year, on summer solstice (the longest day of the year), the sun will rise in alignment with the heel stone as seen from the center of the ring.
In addition to the Sarsen stones there was a less elaborate set of blue stones. Some set in a ring outside the trilithons, and the others in a horseshoe within the thrilithon horseshoe. There are also four “station stones” set in a rectangle outside the ring. The station stones may have been used to predict the movement of the moon.
Perhaps what is strangest about the Stonehenge ring of stones is that it is far from being unique. Though Stonehenge is the most intact and elaborate, there are known to be over a thousand remains of stone rings through out the British Isles and Northern France. Some of them were small, like Keel Cross in County Cork which is just 9 feet in diameter. The largest, Avebury, covers over 28 acres and encircles what is now a whole village. Some of the stones at Avebury weighed 60 tons.
How did the makers move these massive rocks many miles? Probably by dragging them on wooden sledges. Before the first one could be moved, though, a road had to be cleared from, what was then, a thick forest. Not an easy job in itself. Especially for a people who probably spent most of their time and energy just fighting for survival. The construction of both Avebury and Stonehenge must have been the work of many generations.
Archaeologist Clive Waddington has suggested that the earliest henges, simple ditches with surrounding mounds, my have been stock enclosures for cattle. Remains of fence and gates found at the Coupland Henge, which is more than 800 years older than Stonehenge, support his idea. Waddington thinks when cattle were moved into the enclosure during certain seasons, rituals were performed. As time went on the circles functional aspect faded away and they became purely religious structures.
Most of the rings were smaller than Avebury and simpler than Stonehenge. While some of them had astronomical alignments built into their design, many did not. This suggests that their use as observatories may have been a secondary function. Perhaps, for some, Waddington’s corrals were the primary function, though, we may never be able to say for sure. As Professor Richard Atkinson, of University College, Cardiff, a researcher at Stonehenge, once said, “You have to settle for the fact that there are large areas of the past we cannot find out about...”
==============================
The Riddle of the Sphinx


Your fearful form is the work of the deathless gods. To spare the flat and fertile lands they placed you in your depression. A rocky island from which they banished the sand. They placed you as a neighbor to the pyramids...Who vigilantly watches the blessed Osiris...
-- Inscription from the second century A.D.
After 25 centuries the history of the great Sphinx at Giza was so forgotten that many believed it had been placed in its position, as guardian of the pyramids, by the Gods. Indeed, the Sphinx is such an impressive work one, even today, might easily believe it must have been created by supernatural means. The statue, with a man’s head and a lion’s body, stands 66 feet high and 240 feet long. The head measures 19 feet from forehead to chin. Each paw extends 56 feet forward of the body. The face is over 6 yards wide.
The lion was a powerful symbol in ancient Egypt as it represented strength and courage. The great cat was also considered the supreme guardian and tamed lions sometimes accompanied kings into battle. Not just as a mascot, but as the physical presence of a god meant to protect troops. The Sphinx was the combination of two symbols, a lion god, and the king pharaoh/god, into one icon. In fact, the Great Sphinx at Giza probably bears the face of the ruling pharaoh at the time of construction: Chephren.
The symbol wasn’t limited to Egypt, but was also found in ancient Phoenician, Syrian, and Greek societies. In Greek legend, the Sphinx devoured all travelers who could not answer the riddle it posed: “What is the creature that walks on four legs in the morning, two legs at noon and three in the evening?” The hero Oedipus gave the answer, “Man,” causing the Sphinx’s death.
The Great Sphinx at Giza started as a natural outcropping of rock. The ancient Egyptians carved the giant statue into the stone around 2500 B.C.. To make it even taller than the height of the outcrop they chipped out a depression around the base of the statue. The paws were constructed from stone blocks. The entire statue was painted in ancient times: red for the face and body, yellow with blue stripes on the headress. Finally, a temple was built in front of the statue as a place visitors could offer gifts to the “living image” of the creature the Egyptians sometimes referred to as “Horus-in-the-Horizon.”
As time passed the statue was given less attention and, after a few centuries, desert sands covered the Great Sphinx up to its neck. Legends claim that visitors would press their ear to the statue’s lips seeking wisdom. Around 1400 B.C. a Egyptian prince, on a hunt, came to rest in the shadow of the Sphinx. While napping he heard the Sphinx tell him it would make him ruler of Egypt ahead of his older brothers if he promised to clear the sand away. On waking the prince vowed to keep the bargain. Sure enough, as the story goes, he ascended the throne as Pharaoh Thutmose IV and quickly had the statue uncovered.
Historians beleive that Thutmose IV concocted the dream to cover up murder. Thutmose had his brother killed so that he could gain the crown. While the Egyptian people might not have been able to forgive Thutmose the slaying for personal gain, they could overlook it if it seemed like it was the will of the gods.
By the 19th century, when European archaeologists started taking a close look at Egyptian monuments, the statue was again covered up to it’s neck in sand. Efforts to uncover and repair the statue were undertaken early in the 20th century. Preservation work continues even today.
There have been rumors of passageways and secret chambers surrounding the Sphinx and during recent restoration work several tunnels have been re-discovered. One, near the rear of the statue extends down into it for about nine yards. Another, behind the head, is a short dead-end shaft. The third, located mid-way between the tail and the paws, was apparently opened during restoration work in the 1920’s, then resealed. It is unknown whether these tunnels were constructed by the original Egyptian designers, or were cut into the statue at a later date. Many scientists speculate they are the result of ancient treasure hunting efforts.
Several attempts have been made to use non-invasive exploration techniques to ascertain if there are other hidden chambers or tunnels about the Sphinx. These include electromagnetic sounding, seismic refraction, seismic reflection, refraction tomography, electrical resistivity and acoustical survey tests.
Studies made by Florida State University, Waseda University (Japan), and Boston University, have found “anomalies” around the Sphinx. These could be interpreted as chambers or passageways, but they could also be such natural features as faults or changes in the density of the rock. Egyptian archaeologists, charged with preserving the statue, are concerned about the danger of digging or drilling into the natural rock near the Sphinx to find out if cavities really exist.
Are these “anomalies” secret chambers? And is it worth risking damage to such a work as the Sphinx in order to find out? That’s the modern riddle of the Sphinx the Egyptian authorities must solve.
The Sphinx: Older Than We Think?
Conventional science has held that the Sphinx was carved out of an outcropping during the reign of King Khafre around 2500 B.C. In 1979, though, an amateur archaeologist named John Anthony West wrote a book entitled Serpent in the Sky. In the book West suggested that the Sphinx was far older than the pyramids and its severe erosion was the result of rain, not blowing sand. Therefore, concluded West, the Sphinx must have been built thousand of years earlier when the land was much wetter.
Nobody gave West’s theory much attention until West brought in a trained geologist from Boston University named Robert Schoch. Schoch examined the Sphinx and thinks some of the fissures in the rock were indeed created by running water or rain. His conclusion is that the front and side of the Sphinx dated from 5000 to 7000 BC and was remodeled during Khafre’s era to give the likeness of the pharaoh. Other Egyptologists argue that the original estimate is still right and that the fissures found by Schoch were the result of wet sand being blown up from the Nile river, not rain.
==============================